Intro to YAP The building block for Hebrew NLP
Credits and Full Disclosure
YAP, also known as Yet Another (natural language) Parser, is an automatic natural language processing tool tailored for Modern Hebrew texts. YAP can automatically annotate Hebrew texts with different kinds of information, including Lemma, Part of Speech tags (Verb, Noun, etc), Morphological Features (gender, number, etc), as well as Syntactic Relations (Subject, Object, Modifier). YAP has been developed at the ONLP research lab led by Prof. Reut Tsarfaty. The original development of YAP was done by Amir More, and later developments were undertaken by Amit Seker. An overview of YAP, its best practices, and the main ways it is used can be found in this document. Texts and images on this page are adopted and adapted from the full documentation provided by the ONLP lab website and its associated github page here. A YAP online demo by the ONLP lab can be found here. While YAP is open-source, any use of YAP in an academic publication or otherwise should cite this article.
Synopsis
YAP is a natural language parser that is designed to automatically process Hebrew texts. It is an extremely powerful tool which allows users to automatically analyze textual data in Hebrew and annotate it with different levels of analysis.
Specifically, YAP provides the following levels of analysis: Morphological Segmentation, Part of Speech Tagging, Morphological Analysis, and syntactic analysis in the form of Dependency Parse Trees.
History
YAP was implemented for testing the hypothesis of Joint Morpho-Syntactic Processing of Morphologically Rich Languages (MRLs) in a Transition Based Framework. The hypothesis, in a nutshell, is that processing both the morphological and syntactic levels in a joint model would be superior to a pipeline with two independent components. The parser was developed as part of Amir More’s MSc thesis at IDC Herzliya under the supervision of Prof. Reut Tsarfaty, now a professor at Bar-Ilan University and a visiting Professor at Google. The models and training regimes have been tuned and improved by Amit Seker from the Open University and the Bar-Ilan research team. YAP is currently maintained and supported as part of the ONLP lab (The NLP research lab at the Bar Ilan University) toolkit.
A paper on the morphological analysis and disambiguation aspect for Modern Hebrew and Universal Dependencies was accepted to COLING 2016. A follow up paper on the complete morpho-syntactic framework was published at TACL, titled Joint Transition-Based Models for Morpho-Syntactic Parsing: Parsing Strategies for MRLs and a Case Study from Modern Hebrew. Yap contains an implementation of the framework and parser of zpar from Z&N 2011 (Transition-based Dependency Parsing with Rich Non-local Features by Zhang and Nivre, 2011) with flags for precise output parity (i.e. bug replication), trained on the morphologically disambiguated Modern Hebrew treebank.
YAP Overview
A Hebrew sentence can be analyzed using YAP in the following ways:
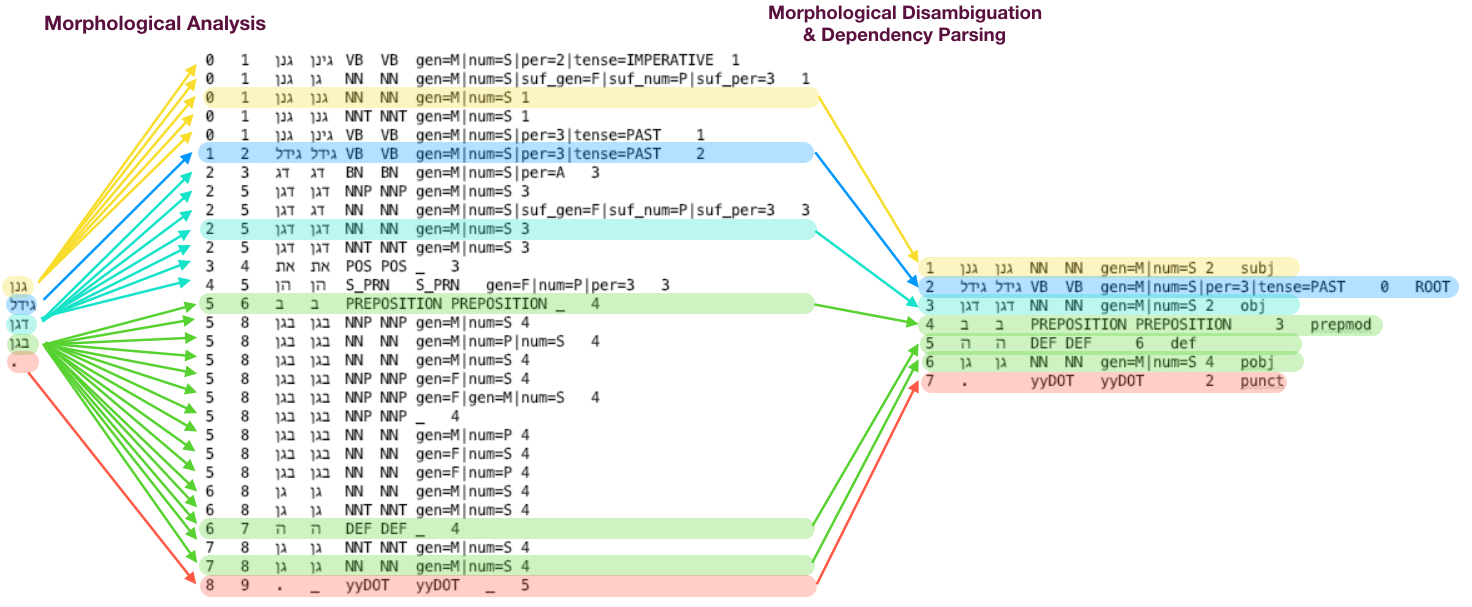
Morphological Analysis
Morphological Analysis shows all the options of interpretations for each word in the sentence.
 For example the sentence “קניתי ארוחה טעימה אתמול”:
For example the sentence “קניתי ארוחה טעימה אתמול”:
0 1 קניתי קנה VB VB gen=F|gen=M|num=S|per=1|tense=PAST 1
0 1 קניתי קנייה NN NN gen=F|num=S|suf_gen=F|suf_gen=M|suf_num=S|suf_per=1 1
1 2 ארוחה ארוחה NN NN gen=F|num=S 2
2 3 טעימה טעימה NN NN gen=F|num=S 3
2 3 טעימה טעים JJ JJ gen=F|num=S 3
3 4 מ מ PREPOSITION PREPOSITION _ 4
3 5 מאוד מאוד RB RB _ 4
4 5 אוד אוד NNT NNT gen=M|num=S 4
4 5 אוד אוד NN NN gen=M|num=S 4
The columns are represented as follows:
- Column 1-2: From/To - The start and end nodes of the morpheme. The numbers are with respect to the maximal length route.
- Column 3: Form - the surface form of the morphological segment.
- Column 4: Lemma.
- Column 5-6: Part of Speech.
- Column 7: Morphological Features.
- Column 8: Token Number - represents the index of the raw (space-delimited) token in the input before segmentation
You can find more information about Morphological Analysis by visiting:
Morphological Disambiguation
Morphological Disambiguation is the next step after a full Morphological Analysis.
Morphological Disambiguation narrows down the options for each word in the sentence based on the Morphological Analysis.
For example the sentence “קניתי ארוחה טעימה אתמול”
0 1 קניתי קנה VB VB gen=F|gen=M|num=S|per=1|tense=PAST 1
1 2 ארוחה ארוחה NN NN gen=F|num=S 2
2 3 טעימה טעים JJ JJ gen=F|num=S 3
3 4 מאוד מאוד RB RB _ 4
The columns are represented as follows:
- Column 1: Morpheme Index in the Sentence.
- Column 2: Form of the Morpheme.
- Column 3: Lemma of the Morpheme.
- Column 4: Coarse Part of Speech Tag.
- Column 5: Fine Part of Speech Tag.
- Column 6: Morphological Features.
- Column 7: Head Index Pointer.
- Column 8: Dependency relation to the HEAD.
- Column 9: Projective Head Unused.
- Column 10: Dependency relation to the PHEAD Unused.
Useful Links
- The original repository.
- A live demo of parsing Hebrew texts is provided here.
- API Website.
- A Forked Repository with CORS enabled + extra features.
At the stage of morphological analysis, there were two possible interpretations of the form ״קניתי״:
Line 1 - A verb, inflected for first person past tense, lemma=״קנה״ (translated as “I bought”);
Line 2 - A noun with a possessive suffix, lemma=״קנייה״ (translated as ‘my purchase’).
There were also two possible interpretations of the form ״טעימה״:
Line 4 - A feminine noun, lemma=״טעימה״ (translated for example as ‘a bite’),
Line 5 - An adjective, inflected for feminine gender, lemma=״טעים״ (translated as ‘tasty’).
At the stage of morphological disambiguation, in the case of ״קניתי״ the interpretation presented in line 1 is selected, and in the case of ״טעימה״ the interpretation presented in line 5 is selected
The columns are represented as follows:
- Column 1-2: From/To - The start and end nodes of the morpheme. The numbers are with respect to the maximal length route.
- Column 3: Form of the Morpheme - the surface form of the morphological segment.
- Column 4: Lemma of the Morpheme.
- Column 5: Coarse Part of Speech Tag.
- Column 6: Fine Part of Speech Tag.
- Column 7: Morphological Features.
- Column 8: Source Token Index.
To find more on Morphological Disambiguation:
- Morphological Disambiguation of Hebrew.
- An Unsupervised Morpheme-Based HMM for Hebrew Morphological Disambiguation.
Dependency Parsing
Dependency Parsing is the process of analyzing the grammatical structure of a sentence to identify related words and their relationship type. YAP returns a dependency tree of the inputted sentence. To find more information on Hebrew Dependency Parsing:
- Hebrew Dependency Parsing: Initial Results.
- Natural Language Processing — Dependency Parsing.
- What’s Wrong with Hebrew NLP — And How to Make it Right.
The Dependency labels of used for YAP originate from this paper:
For example the sentence “אכלתי ארוחה טעימה אתמול”
1 קניתי קנה VB VB gen=F|gen=M|num=S|per=1|tense=PAST 0 ROOT _ _
2 ארוחה ארוחה NN NN gen=F|num=S 1 obj _ _
3 טעימה טעים JJ JJ gen=F|num=S 2 amod _ _
4 מאוד מאוד RB RB 3 mod _ _
YAP via Docker
YAP is currently available as an API service. It can be implemented as a code-based service and accessed as an internet service. For simplicity, you may also use our Docker image. Use the following command to run YAP via Docker:
$ docker run --name yap --restart always -d -p 8000:8000 public.ecr.aws/nnlp-il/nlp_yap_api:latest
Using YAP
YAP’s API exposes an API service. The following wrappers simplify using YAP by exposing simple functions which call the API service.
Python Wrapper - credit to Amit Shkolnik
The wrapper sends the API a joint command, parses the response, and outputs the following:
- Tokenized Text.
- Segmented Text.
- Lemmas.
- Dependency tree.
- md command result.
- ma command result.
To Run the python wrapper use the following code:
text1 = 'היום הם הולכים לקניון'
ip='127.0.0.1:8000'
yap=YapApi()
tokenized_text, segmented_text, lemmas, dep_tree, md_lattice, ma_lattice=yap.run(text1, ip)
The output:
tokenized_text
היום הם הולכים לקניון
segmented_text
היום הם הולכים ל ה קניון
lemmas
היום הוא הלך ל ה קניון
dep_tree
num word lemma pos pos_2 empty dependency_arc dependency_part dependency_arc_2 dependency_part_2
0 1 היום היום RB RB 3 tmod _ _
1 2 הם הוא PRP PRP gen=M|num=P|per=3 3 subj _ _
2 3 הולכים הלך BN BN gen=M|num=P|per=A 0 ROOT _ _
3 4 ל ל PREPOSITION PREPOSITION 3 prepmod _ _
4 5 ה ה DEF DEF 6 def _ _
5 6 קניון קניון NN NN gen=M|num=S 4 pobj _ _
md_lattice
num num_2 word empty pos ... num_s_p per tense num_last lemma
0 0 1 היום -1 RB ... -1 -1 -1 1 היום
1 1 2 הם -1 PRP ... P 3 -1 2 הוא
2 2 3 הולכים -1 BN ... P A -1 3 הלך
3 3 4 ל -1 PREPOSITION ... -1 -1 -1 4 ל
4 4 5 ה -1 DEF ... -1 -1 -1 4 ה
5 5 6 קניון -1 NN ... S -1 -1 4 קניון
[6 rows x 12 columns]
ma_lattice
num num_2 word lemma ... num_last suf_gen suf_num suf_per
0 0 1 ה ה ... -1 -1 -1 -1
1 0 2 ה ה ... -1 -1 -1 -1
2 0 3 היום היום ... -1 -1 -1 -1
3 1 3 יום יום ... -1 -1 -1 -1
4 1 3 יום יום ... -1 -1 -1 -1
5 2 3 יום יום ... -1 -1 -1 -1
6 2 3 יום יום ... -1 -1 -1 -1
7 3 4 הם הוא ... -1 -1 -1 -1
8 3 4 הם הוא ... -1 -1 -1 -1
9 4 5 הולכים הלך ... -1 -1 -1 -1
10 4 5 הולכים הלך ... -1 -1 -1 -1
11 5 6 ל ל ... -1 -1 -1 -1
12 5 8 לקניון לקניון ... -1 -1 -1 -1
13 5 8 לקניון לקניון ... -1 -1 -1 -1
14 5 8 לקניון לקניון ... -1 -1 -1 -1
15 5 8 לקניון לקניון ... -1 -1 -1 -1
16 5 8 לקניון לקניון ... -1 -1 -1 -1
17 5 8 לקניון לקניון ... -1 -1 -1 -1
18 5 8 לקניון לקניון ... -1 -1 -1 -1
19 5 8 לקניון לקניון ... -1 -1 -1 -1
20 5 8 לקניון לקניון ... -1 -1 -1 -1
21 6 7 ה ה ... -1 -1 -1 -1
22 6 8 קניון קניון ... -1 -1 -1 -1
23 6 8 קניון קניון ... -1 -1 -1 -1
24 7 8 קניון קניון ... -1 -1 -1 -1
25 7 8 קניון קניון ... -1 -1 -1 -1
[26 rows x 15 columns]
R Wrapper - credit to Almog Simchon
The wrapper sends the API a joint command, parses the response, and outputs the following:
- Lemmas.
- CoNLL style dependency tree.
- Lattice style dependency tree. To Run the R wrapper use the following code: ```console text <- “גנן גידל דגן בגן” token <- “YourAPIToken” yap_list <- yap(text, token)
yap_lemmas(yap_list) #get lemmas dep_conll(yap_list) #get CoNLL style dependency tree dep_lattice(yap_list) #get Lattice style dependency tree
The results should be the same as the python wrapper’s results.
The API url can be changed inside the file ```console/yappr/R/yap.R ```
```console
url <- paste0('https://www.langndata.com/api/heb_parser?token=',Token)
The url needs to be the url of the YAP API you wish to use
JavaScript/TypeScript Client -
An NPM library can be used to see both the Morphological Analysis The Morphological Disambiguation and the Dependency Tree into an easy-to-use data structure. To install the Client we need to install it via npm:
npm i @nnlp-il/yap-js-client
Usage of the NPM library in an example:
const { YapClient } = require("@nnlp-il/yap-js-client");
const test = async () => {
const client = new YapClient('http://localhost:8000');
const result = await client.jointAnalysis("גנן גידל גנן בגן");
console.log(result);
}
test();
YAP as a Web Service
YAP API exists as a web service. The service requires registration and has the following limitations:
- 1 call per 3 seconds.
- 250 words max per call.
- Long text requires longer processing time, Set the HTTP call timeout accordingly.
Running YAP Commands Manually
We can run the commands from the terminal/cmd using a local text file and analyze it.
Using the command line, you can process one input file at a time.
Note it is possible to have multiple sentences in a single file.
The original YAP repository contains a manual on how to run YAP in the command line manually.
Please ensure that you have Go and Git installed and on your command PATH.
If you are new to GOlang:
Set up your environment with one of these guides:
- GopherGuides
- Tutorialspoint Troubleshooting For Running YAP Manually:
If the setup is not working it is usually either 1 of these 3 things:
- Go version is above 1.15.
- GOPATH is not set up correctly.
- bzip2 is not installed on your pc.
If bunzip does not work the extraction of the bzip files can be done manually which allows you to delete the
console bunzip2 data/*.bz2line.Running YAP API Manually
YAP can run as a server listening on port 8000:
$ ./yap apiTo change the port from 8000 we need to yap/webapi/webapi.go and change the 8000 to the wanted port (line 12 here):
func StartAPIServer(cmd *commander.Command, args []string) error { HebrewMorphAnalyazerInitialize(cmd, args) MorphDisambiguatorInitialize(cmd, args) DepParserInitialize(cmd, args) JointParserInitialize() router = mux.NewRouter() router.HandleFunc("/yap/heb/ma", HebrewMorphAnalyzerHandler) router.HandleFunc("/yap/heb/md", MorphDisambiguatorHandler) router.HandleFunc("/yap/heb/dep", DepParserHandler) router.HandleFunc("/yap/heb/pipeline", HebrewPipelineHandler) router.HandleFunc("/yap/heb/joint", HebrewJointHandler) log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8000", router)) return nilUsing Yap Summary
To summarize, YAP can be used YAP in a variety of ways:
- Install YAP and run it manually via command line.
- Install YAP and run it via API.
- Sign Up and use the YAP API here
Here is a comparison for using YAP:
| Category/YAP Usage | Manually | Local API | Remote API |
|---|---|---|---|
| Need Installation | Yes | Yes | No |
| RAM Usage | 2.5GB | 5GB | 1GB |
| Changeable Code | Yes | Yes | No |
| Can use Different Models | Yes | Yes | No |
| Can be used with current Wrappers | No | Yes | Yes |
| Speed | Fast | Fast | Slow |
